
# Flag that indicates whether to use reaper. # .dynamo-db.table-name=DynamoDbCasMfaTrustRecords # The table name used and created by CAS to hold mfa trust definitions in DynamoDb. # Optionally specifies the proxy username to connect through.
Splunk rex password#
# Optionally specifies the proxy password to connect through. # Optionally specifies the proxy host to connect through. # .dynamo-db.prevent-table-creation-on-startup=false # Flag that indicates whether to prevent CAS from creating tables. # Indicates that the database instance is local to the deployment that does not require or use any credentials or other configuration other than host and region. # .dynamo-db.drop-tables-on-startup=false # Flag that indicates whether to drop tables on start up. # .dynamo-db.client-execution-timeout=10000 # Billing mode specifies how you are charged for read and write throughput and how you manage capacity.

On-demand mode is a good option if any of the following are true:
You can use auto scaling to automatically adjustĬapacity based on the specified utilization rate You can forecast capacity requirements to control costs.You run applications whose traffic is consistent or ramps gradually.You have predictable application traffic.Provisioned mode is a good option if any of the following are true: PROVISIONED: Provisioned mode means that you specify the number of readsĪnd writes per second that you expect your.
Splunk rex how to#
If you’d like more information about how to leverage regular expressions in your Splunk environment, reach out to our team of experts by filling out the form below.Billing mode specifies how you are charged for read and write throughput and how you manage capacity. There are plenty of self-tutorials, classes, books, and videos available via open sources to help you learn to use regular expressions. It is a skill set that’s quick to pick up and master, and learning it can take your Splunk skills to the next level. Using regex can be a powerful tool for extracting specific strings. Use to practice your RegEx: Figure 5 – a practice search entered into We’re Your Regex(pert) Syntax for the command: | rex field=field_to_rex_from “FrontAnchor(? = searches for digits that are 1-3 in length, separated by periods.
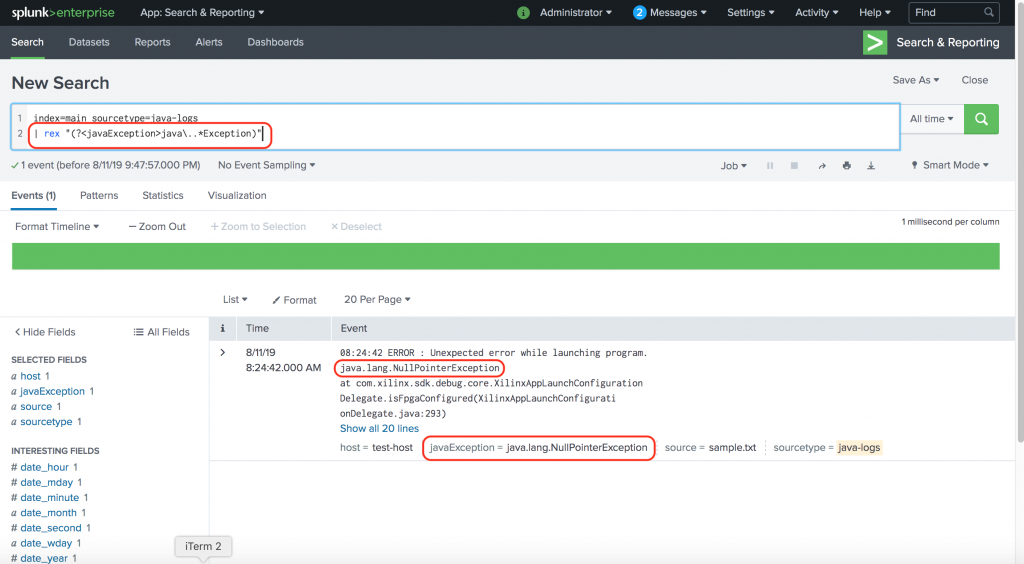
When using regular expression in Splunk, use the rex command to either extract fields using regular expression-named groups or replace or substitute characters in a field using those expressions. I have sorted them into a table, to show that other CVE_Number fields were extracted: Figure 2 – the job inspector window shows that Splunk has extracted CVE_Number fields The rex Commands Next, by using the erex command, you can see in the job inspector that Splunk has ‘successfully learned regex’ for extracting the CVE numbers. I want to have Splunk learn a new regex for extracting all of the CVE names that populate in this index, like the example CVE number that I have highlighted here: Figure 1 – a CVE index with an example CVE number highlighted In this screenshot, we are in my index of CVEs. Syntax for the command: | erex examples=“exampletext1,exampletext2”

When using regular expression in Splunk, use the erex command to extract data from a field when you do not know the regular expression to use. Let’s get started on some of the basics of regex! How to Use Regex The erex command In Splunk, regex also allows you to conduct field extractions on the fly. Regex is a great filtering tool that allows you to conduct advanced pattern matching. A Regular Expression (regex) in Splunk is a way to search through text to find pattern matches in your data. Especially data that’s hard to filter and pair up with patterned data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
